RFID TECHNOLOGY
Introduction
New technologies have always been of interest for libraries, both for the potential of increasing the quality of service and for improving efficiency of operations. At present libraries
of all kinds whether public, research or special libraries are overwhelmingly looking forward to adopt new technologies due to its potential for cost savings in the operations and
the management of books and patrons. One such technology which is gaining tremendous popularity among the various libraries is RFID technology since it revolutionizes the way a library operates.
Pain Areas
� Time Consuming Stock Verification Process: Often in a library with big no of collections, manual stock verification becomes a tedious task which may take more than a week to get completed
during which the library may have to be shut down for the members leading to inconvenience to them.
� Weak Security: Especially during peak hours when there is a lot of crowd in the library some students try to move away with the books without issuing it. It is a pain to keep track of such
unauthorized movements.
� Long queues for book issue and return: Manual issue and return of books is a slow process leading to long queues in front of the counter during peak hours. This is a waste of time for the
member as well as the library staff who can fruitfully utilize this time for their internal processes.
� Tracking a misplaced book: It often happens that a book say for example of fiction is wrongly placed in the non
� fiction segment or the children's book segment. The patron generally has
a tough time locating such misplaced books.
� Getting information regarding a particular book: Many a times a member may be looking for a particular book but may not have complete information about it.
RFID Technology
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a generic term that is used to describe a system that transmits the identity (in the form of a unique serial number) of an object or person wirelessly in
a tag, using radio waves. Tags or Transponders are microchips with an antenna which have a unique Identifier Number and memory which can be programmable according to the customer requirement.
Tags are then affixed to the books either in the inside or hard bound in them.
New technologies have always been of interest for libraries, both for the potential of increasing the quality of service and for improving efficiency of operations. At present libraries
of all kinds whether public, research or special libraries are overwhelmingly looking forward to adopt new technologies due to its potential for cost savings in the operations and
the management of books and patrons. One such technology which is gaining tremendous popularity among the various libraries is RFID technology since it revolutionizes the way a library operates.
Pain Areas
� Time Consuming Stock Verification Process: Often in a library with big no of collections, manual stock verification becomes a tedious task which may take more than a week to get completed
during which the library may have to be shut down for the members leading to inconvenience to them.
� Weak Security: Especially during peak hours when there is a lot of crowd in the library some students try to move away with the books without issuing it. It is a pain to keep track of such
unauthorized movements.
� Long queues for book issue and return: Manual issue and return of books is a slow process leading to long queues in front of the counter during peak hours. This is a waste of time for the
member as well as the library staff who can fruitfully utilize this time for their internal processes.
� Tracking a misplaced book: It often happens that a book say for example of fiction is wrongly placed in the non
� fiction segment or the children's book segment. The patron generally has
a tough time locating such misplaced books.
� Getting information regarding a particular book: Many a times a member may be looking for a particular book but may not have complete information about it.
RFID Technology
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a generic term that is used to describe a system that transmits the identity (in the form of a unique serial number) of an object or person wirelessly in
a tag, using radio waves. Tags or Transponders are microchips with an antenna which have a unique Identifier Number and memory which can be programmable according to the customer requirement.
Tags are then affixed to the books either in the inside or hard bound in them.
Proposed Solution
Book Tagging
1.Every Book has an Accession Number which is a unique serial number
2. Every book is pasted with RFID tags. Tag Id is mapped to book id and its attributes in the database
Library Members
1. Every member will have a unique member ID
2. A member card (RFID card with unique Card ID) will be issued to each member
3. Card ID will be mapped to the member id in the database
Book Issue/Return
1. Member will come to the issue/return counter with the member card and Books
2. Counter operator will scan the member card and the books using the desktop RFID reader attached to the system
Self Check in/Check out
1. Member will come to the self check in/check out counter with the member card and the books
2. He will scan the member id card and the books to make the issue/return
Book Drop
1. A member can simply drop the book in the Book drop box for returning the book
2. RFID reader installed in the book drop box will automatically read the book id and it will be marked as returned
Anti Theft control
1. A long range RFID reader will be installed at the exit gate
2. This reader will read all the books passing through the gate
3.If any book read is not marked as issued in the system, an audible alarm will be generated.
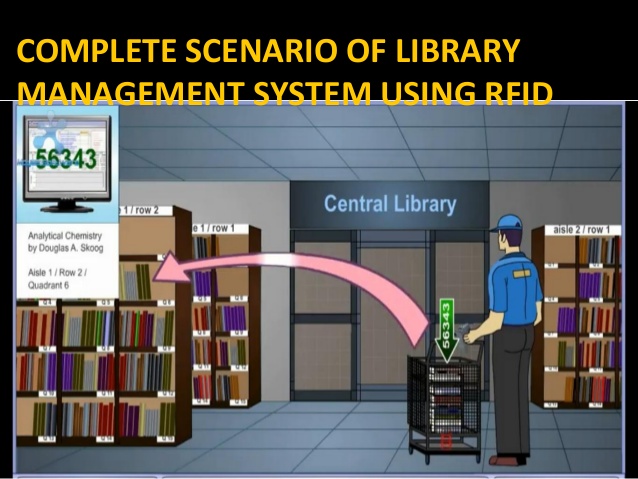
Finding a book
1.ID of the book to be find will be inputted to a hand held portable RFID reader
2. User will move near the book racks with the portable reader
3. Reader will read the book ids of the books in racks
4. When the reader reads the initially inputted book id, it will make an audible alarm
Physical Verification
1.Handheld portable RFID reader will be used for taking the physical inventory of the books
2. User will show the portable reader to all books without removing the books from the racks
3.After collecting all book ids, the reader will be connected to the server to transfer the data to the software and reports will be generated in software.
ADVANTAGE OF RFID IN LIBRARIES
High speed inventory: A unique advantage of RFID systems is their ability to scan books on the shelves without tipping them out or removing them. A hand-held inventory reader can be moved rapidly across a shelf of books to read all of the unique identification information. Using wireless technology, it is possible not only to update the inventory, but also to identify items, which are out of proper order.
Self check in and check out: It helps patrons to get their books issued or returned without the help of the library staff. This reduces patron queues and improves productivity.
High Security: The gate antennas provided at the entry/exit points will prevent any unauthorized movement of books out of the library thus ensuring high security and eliminating loss due to shrinkage and theft. Incase any patron tries to walk away with a book without properly issuing an alarm would be raised at the exit gate.
Book Drop Box for book return: Since a drop box allows patrons to return the books and get an automated receipt without the help of a library staff, it helps the library staff to contribute that time to more productive duties. It leads to cutting of queues enhancing customer satisfaction as well.
Patron Experience: The biggest advantage that an automated library holds is increased patron satisfaction. Tracking books is no longer a pain for the patron. The patron has a pleasant experience when (s)he walks in a library that is completely automated with smooth work-flows and no queues at the book issue counter.
Image Enhancement: Smooth work-flows and increased patron satisfaction helps in enhancing the image of the library and hence the institution among all other leading libraries of the country.
Tag life: RFID tags last longer than barcodes because the technology does not require line-of sight. Most RFID vendors claim a minimum of 100,000 transactions before a tag may need to be replaced.
Book Tagging
1.Every Book has an Accession Number which is a unique serial number
2. Every book is pasted with RFID tags. Tag Id is mapped to book id and its attributes in the database
Library Members
1. Every member will have a unique member ID
2. A member card (RFID card with unique Card ID) will be issued to each member
3. Card ID will be mapped to the member id in the database
Book Issue/Return
1. Member will come to the issue/return counter with the member card and Books
2. Counter operator will scan the member card and the books using the desktop RFID reader attached to the system
Self Check in/Check out
1. Member will come to the self check in/check out counter with the member card and the books
2. He will scan the member id card and the books to make the issue/return
Book Drop
1. A member can simply drop the book in the Book drop box for returning the book
2. RFID reader installed in the book drop box will automatically read the book id and it will be marked as returned
Anti Theft control
1. A long range RFID reader will be installed at the exit gate
2. This reader will read all the books passing through the gate
3.If any book read is not marked as issued in the system, an audible alarm will be generated.
Finding a book
1.ID of the book to be find will be inputted to a hand held portable RFID reader
2. User will move near the book racks with the portable reader
3. Reader will read the book ids of the books in racks
4. When the reader reads the initially inputted book id, it will make an audible alarm
Physical Verification
1.Handheld portable RFID reader will be used for taking the physical inventory of the books
2. User will show the portable reader to all books without removing the books from the racks
3.After collecting all book ids, the reader will be connected to the server to transfer the data to the software and reports will be generated in software.
ADVANTAGE OF RFID IN LIBRARIES
High speed inventory: A unique advantage of RFID systems is their ability to scan books on the shelves without tipping them out or removing them. A hand-held inventory reader can be moved rapidly across a shelf of books to read all of the unique identification information. Using wireless technology, it is possible not only to update the inventory, but also to identify items, which are out of proper order.
Self check in and check out: It helps patrons to get their books issued or returned without the help of the library staff. This reduces patron queues and improves productivity.
High Security: The gate antennas provided at the entry/exit points will prevent any unauthorized movement of books out of the library thus ensuring high security and eliminating loss due to shrinkage and theft. Incase any patron tries to walk away with a book without properly issuing an alarm would be raised at the exit gate.
Book Drop Box for book return: Since a drop box allows patrons to return the books and get an automated receipt without the help of a library staff, it helps the library staff to contribute that time to more productive duties. It leads to cutting of queues enhancing customer satisfaction as well.
Patron Experience: The biggest advantage that an automated library holds is increased patron satisfaction. Tracking books is no longer a pain for the patron. The patron has a pleasant experience when (s)he walks in a library that is completely automated with smooth work-flows and no queues at the book issue counter.
Image Enhancement: Smooth work-flows and increased patron satisfaction helps in enhancing the image of the library and hence the institution among all other leading libraries of the country.
Tag life: RFID tags last longer than barcodes because the technology does not require line-of sight. Most RFID vendors claim a minimum of 100,000 transactions before a tag may need to be replaced.